
Why Do We Get Goosebumps When Cold or Scared?
Introduction
Goosebumps are those pesky little bumps that pop up on your skin when you’re feeling cold or scared. They turn your smooth skin into a mini mountain range, making you look like you’ve just seen a ghost—or maybe just a really big spider. It’s funny how something so small can trigger such a strong response, isn’t it?
You usually get goosebumps when the temperature drops or during emotional moments. Imagine watching a horror movie, and just as the suspense builds, your skin starts to prickle. That’s goosebumps for you! The purpose of this article is to investigate why we experience this peculiar phenomenon, the science behind it, and what it all means for us in the grand scheme of life.

And speaking of horror movies, there’s nothing quite like a good scare to get your heart racing. If you’re looking for a thrilling collection, check out A Classic Horror Movie Collection (Blu-ray). Perfect for those late-night chills!
What Are Goosebumps?
Goosebumps, also known as piloerection or cutis anserina, are an involuntary reaction of our body. They occur when tiny muscles at the base of hair follicles contract, causing the hair to stand upright. Picture a cat trying to look bigger in front of a dog; it’s essentially the same idea.
This reflex is controlled by our sympathetic nervous system, which is our body’s way of preparing for stress or cold. When we feel cold, these muscles tighten, and voilà! The hair stands on end, and we get those charming bumps.
But why do we still have this reaction when we lack the thick fur of our animal ancestors? Well, it’s a throwback to our evolutionary past. Our ancestors had more body hair, and this reaction helped trap warm air close to the skin, providing insulation against the cold. Fun fact: that’s where the term “gooseflesh” comes from! It resembles the skin of a plucked goose, which is not exactly something you’d want to show off at a party.

So, while goosebumps might not serve much purpose for humans today, they’re a fascinating remnant of our evolutionary journey, reminding us that we’re all connected in this wild ride called life. Speaking of warmth, if you find yourself shivering, consider snuggling up with A Cozy Blanket for Cold Weather. It’s the perfect companion for those chilly nights!
Causes of Goosebumps
1. Cold Temperatures
When you feel a chill in the air, your body springs into action. The sympathetic nervous system kicks in, triggering a reflex that causes tiny muscles at the base of your hair follicles to contract. This reaction leads to what we know as goosebumps. But why does this happen?
In animals, such as those with thick fur, this response serves a vital purpose. When their hair stands on end, it traps a layer of warm air close to the skin. This helps them maintain their body heat, acting like a natural insulation system. For humans, who have far less body hair, the effect is less practical. Nonetheless, it’s a remnant of our evolutionary past.

Picture this: you’re outside in the winter, and the temperature drops suddenly. As your body reacts, those goosebumps appear, looking almost like tiny mountains on your skin. They signal your body to generate heat, even if only minimally. Each contract of the arrector pili muscles pulls your hairs up, which is a throwback to when our ancestors had more body hair to keep them warm.
Even though the goosebump phenomenon may seem trivial for modern humans, it serves as a fascinating reminder of our evolutionary history. Imagine a fluffy dog in the cold, trying to stay warm by puffing up its fur. It’s the same principle! To help keep the chill away, you might also enjoy A High-Quality Humidifier for Comfortable Environments. It’s a game changer for those dry winter days!
2. Emotional Responses
Now let’s flip the script. Goosebumps also appear when emotions run high. Feeling scared? Excited? Awe-inspired? All these feelings can elicit goosebumps. The connection here is with the fight-or-flight response, where your body prepares to either confront danger or flee.
When you watch a horror movie, and the suspense builds, your body might react instantly. You might feel your heart racing, and before you know it, those goosebumps pop up. This happens because your brain releases adrenaline, a hormone that causes your arrector pili muscles to contract, just like in the cold.

Think about the last time you heard a song that gave you chills. That’s not just your imagination! The music taps into your emotional state, triggering the same physiological response. Whether it’s a powerful ballad or a nostalgic tune, the emotional impact can be so intense that goosebumps are almost guaranteed. And if you’re looking for the perfect soundtrack to accompany those moments, check out A Collection of Classical Music CDs for Emotional Chills.
You might experience goosebumps when you watch a touching scene in a movie or even during a powerful speech. The combination of music, visuals, and emotions creates a perfect storm for goosebumps. The body’s reaction is like a badge of honor, indicating that something has struck a chord deep within your soul.

So there you have it! From the cold winds of winter to the chills of a thrilling moment, goosebumps are our body’s quirky way of responding to the world around us. They remind us of our primal instincts, making us feel alive in a way that’s both fascinating and just a little funny, too.
3. Other Triggers
Goosebumps aren’t just reserved for chilly weather or scary movies. They can also pop up during unexpected moments of pleasure, like when you feel a rush of nostalgia or experience sexual arousal. Yes, you heard that right! Who knew that a trip down memory lane could give you the same skin reaction as a horror flick?
Interestingly, there’s a phenomenon known as “frisson,” which refers to those delightful chills you get when listening to moving music or admiring a piece of art. Think of it as your body’s way of saying, “Wow, that’s beautiful!” It’s like a mini emotional rollercoaster, where your body reacts to the highs and lows of the melody or the impact of a stunning painting.

Studies have shown that frisson often results in goosebumps due to the brain’s response to emotionally charged moments. For example, a classical piece might evoke memories of a cherished moment in your life, leading to an emotional release that sends goosebumps cascading down your arms. It’s the magic of music!
Anecdotal evidence supports this, with many people reporting goosebumps during pivotal life moments, like watching a heartfelt wedding ceremony or hearing a powerful speech. These experiences tap into our emotional reservoir, triggering the same sympathetic nervous system response that makes us shiver when we’re cold or scared. And if you want to capture those feelings creatively, consider picking up A Set of Art Supplies for Creative Expression.
So, the next time you find yourself getting goosebumps while reminiscing about a first love or getting lost in a beautiful symphony, know that your body is simply celebrating those deep emotional connections!
Modern Implications
In modern humans, goosebumps have lost most of their practical benefits. Imagine trying to retain heat with hair that barely exists! The arrector pili muscles contract, causing the hair to stand up, but for us, this response is like using a flip phone in the age of smartphones—not exactly effective.
However, recent research has uncovered fresh roles for goosebumps that might surprise you. A 2020 study revealed that the same muscle and nerve cells responsible for goosebumps may also stimulate hair follicle regeneration. That’s right! The mechanism we once thought was just a quirky throwback from our furry ancestors might actually play a part in hair growth.
This discovery hints at potential applications in treating hair loss and understanding skin healing. So, while goosebumps may seem like a relic of the past, they could hold the key to some modern-day solutions. Who knew those little bumps could be so multidimensional? And if you want to keep your skin feeling fresh while you’re at it, consider treating yourself to A Home Spa Kit for Relaxation. Because who doesn’t love a little pampering?
Health Concerns Related to Goosebumps
When Goosebumps Indicate a Medical Issue
While goosebumps are typically harmless, there are rare medical conditions where they can signal something more serious. One such condition is temporal lobe epilepsy, where individuals may experience piloerection before or during seizures. This can be an alarming sign, making it crucial to consult a healthcare professional if you notice this happening frequently.
Anxiety disorders can also cause unexpected goosebumps. When anxiety levels escalate, the body reacts with various physiological responses, including those prickly bumps on your skin. This can be particularly distressing for those already grappling with anxiety, as it adds another layer to their experience.

Additionally, withdrawal from certain substances, such as opioids, is often accompanied by goosebumps—a phenomenon colloquially referred to as “cold turkey.” The body’s sudden need to stabilize after stopping substance use can lead to a range of symptoms, including those infamous bumps.
In these cases, goosebumps serve as a reminder to pay attention to our bodies and seek professional help when unusual symptoms arise. Always trust your instincts; your skin may have more to say than you think! And while you’re at it, consider keeping a Journal for Emotional Reflection close by. It can be a great way to process those feelings!
Common Misconceptions
Goosebumps often spark curiosity and misconceptions regarding their relationship to health. Some people think that frequent goosebumps indicate a serious medical condition. However, that’s usually not the case. Goosebumps are primarily a physiological response, not a health alarm.
Many assume that having goosebumps means you are always cold or fearful. While these situations can trigger the response, there are other factors at play. Emotional reactions, such as excitement or nostalgia, can also cause goosebumps. So, if you feel a chill down your spine during a touching moment, don’t worry—it’s perfectly normal!

It’s important to recognize when goosebumps warrant medical attention. If you experience them alongside unusual symptoms like confusion, drowsiness, or difficulty breathing, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional. These signs may indicate underlying conditions, such as hypothermia or anxiety disorders.
In general, goosebumps are harmless and a natural part of our body’s reaction to various stimuli. So, the next time you feel those little bumps, take a moment to appreciate your body’s quirky way of reminding you of your primal instincts!
Conclusion
Understanding why we get goosebumps when cold or scared offers fascinating insights into our biology and evolution. These little bumps, scientifically known as piloerection, remind us of our connection to our animal ancestors, who relied on this response for warmth and defense. Why do we get goosebumps when cold or scared
Goosebumps serve as a visual cue of our body’s reactions to environmental changes and emotional stimuli. Whether you’re watching a suspenseful film or feeling a chill in the air, these bumps are part of our instinctual response system.
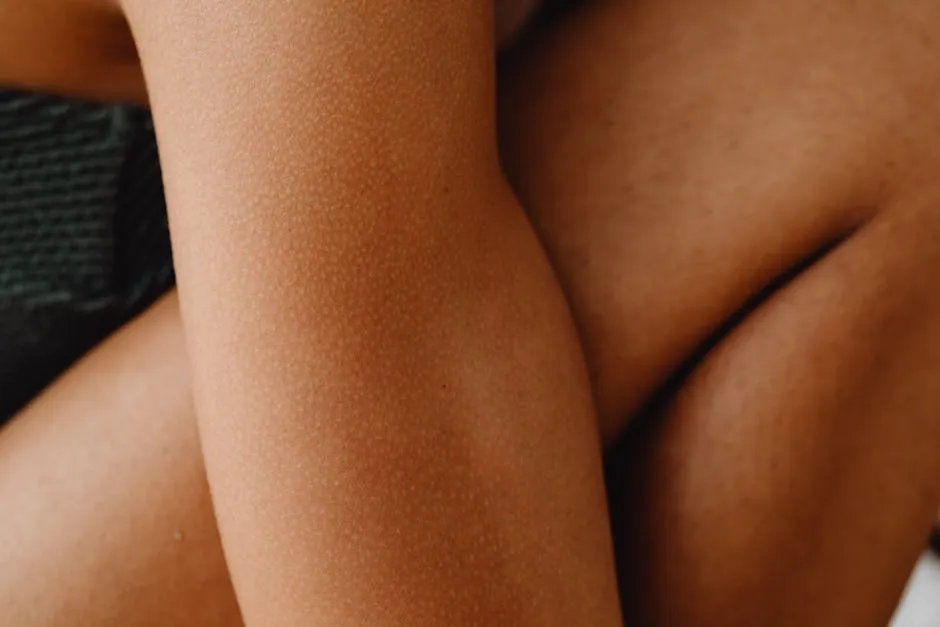

As you reflect on your own experiences with goosebumps, consider the emotions that accompany them. Do they emerge during moments of joy, fear, or nostalgia? By paying attention to these sensations, you can deepen your appreciation for the complex interplay between our emotions and physiological responses.
So, embrace those goosebumps! They are a quirky, fascinating reminder of our shared human experience. And for those who enjoy a bit of mystery and thrill, don’t forget to check out A Subscription Box for Mystery and Thrill Seekers. It could be the perfect way to add a little excitement to your life!
Why are goosebumps more common in some people than others?
Goosebumps can vary in frequency among individuals due to genetic and environmental factors. Genetic predispositions may influence how sensitive a person’s nervous system is to stimuli. For example, some people may have a more reactive sympathetic nervous system, leading to more frequent goosebumps. Environmental conditions also play a role. Those exposed to colder climates might experience goosebumps more often due to temperature fluctuations. Additionally, personal experiences and emotional sensitivity can impact how often one feels goosebumps.
Can you voluntarily induce goosebumps?
Yes, some people can consciously trigger goosebumps! This phenomenon often involves psychological elements, such as recalling a particularly emotional memory or listening to moving music. By focusing on intense feelings or memories, you may activate the sympathetic nervous system, resulting in goosebumps. However, this ability varies among individuals. While some can easily induce this response, others might find it challenging.
Are goosebumps harmful?
Generally, goosebumps are not harmful. They are a natural physiological response to various stimuli, including cold or strong emotions. However, in rare cases, persistent or frequent goosebumps may signal underlying conditions, such as anxiety disorders or temporal lobe epilepsy. If you notice other concerning symptoms alongside goosebumps, such as confusion or seizures, it’s essential to seek medical advice.
Do all animals get goosebumps?
Many animals experience a similar response, although the physiological mechanisms can differ. For instance, furry animals puff up their fur when they feel threatened, making themselves appear larger to potential predators. While most mammals exhibit this response, the degree of effectiveness varies. For humans, with our relatively sparse body hair, the practical benefits of goosebumps are minimal. Nonetheless, the response is a shared evolutionary trait among mammals.
What role do emotions play in triggering goosebumps?
Emotions significantly impact the likelihood of experiencing goosebumps. Intense feelings—like fear, excitement, or nostalgia—can activate the sympathetic nervous system, causing the arrector pili muscles to contract. This reaction often serves as a physical manifestation of emotional arousal. For example, you might experience goosebumps during a powerful musical performance or a heartwarming moment in a film. The connection between emotional states and physiological responses highlights the intricate relationship between our feelings and bodies.
Please let us know what you think about our content by leaving a comment down below!
Thank you for reading till here 🙂
All images from Pexels




